Blood Pressure
Find a wide range of reliable blood pressure monitors and accessories to help you track and manage your health effectively. Shop high-quality devices designed for accuracy and ease of use, available at competitive prices. Ensure your well-being with trusted products for home or professional use.
Blood pressure management is crucial for preventing heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems. Various medications help control high blood pressure effectively. This review covers popular pills widely used for this condition.
Aceon (perindopril) is an ACE inhibitor. It relaxes blood vessels, making it easier for the heart to pump blood. Patients often report improved blood pressure readings. It is usually well tolerated but may cause a dry cough or dizziness in some.
Adalat (nifedipine) is a calcium channel blocker. It lowers blood pressure by relaxing the arteries. Adalat is useful for patients with angina and hypertension. It may cause flushing, headache, or swelling in the ankles.
Aldactone (spironolactone) is a potassium-sparing diuretic. It reduces fluid buildup and lowers blood pressure. Aldactone can help patients with resistant hypertension. Common side effects include increased urination and, in some cases, hormonal changes.
Altace (ramipril) is another ACE inhibitor. It is known for protecting the heart and kidneys while lowering blood pressure. Side effects are similar to other ACE inhibitors, including cough and low blood pressure symptoms.
Avapro (irbesartan) is an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB). It helps relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure without causing cough. Avapro is preferred for patients who cannot tolerate ACE inhibitors.
Beloc (metoprolol) is a beta-blocker. It reduces heart rate and the heart’s workload to control blood pressure. It is also used after heart attacks. Side effects can include fatigue, cold hands, and sleep disturbances.
Benicar (olmesartan) is an ARB that effectively reduces blood pressure. It is noted for once-daily dosing and few side effects. Some patients might experience dizziness or gastrointestinal issues.
Calan and Calan SR (verapamil) are calcium channel blockers. They control blood pressure and chest pain. The SR form is extended-release, providing steady blood pressure control. Side effects may include constipation and swelling.
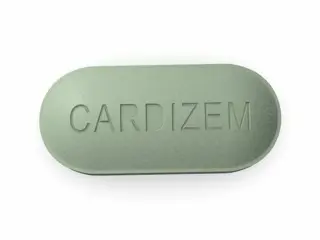
Cardizem (diltiazem) is also a calcium channel blocker. It helps widen blood vessels and reduce heart rate. Cardizem is useful in treating hypertension and certain heart rhythm disorders. Common issues include dizziness and tiredness.
Cartia XT is a sustained-release diltiazem variant. It offers smoother blood pressure control over 24 hours with fewer doses.
Catapres and Clonidine are central alpha agonists. They lower blood pressure by acting on the brain. Clonidine is effective but may cause dry mouth, sedation, or rebound hypertension if stopped abruptly.
Combipres is a combination drug containing beta-blocker and diuretic components. It is useful when a single agent is not sufficient. Side effects reflect those of its individual drugs.
Coreg (carvedilol) is a non-selective beta-blocker with alpha-blocking effects. It is often used in heart failure and hypertension. Coreg can cause fatigue, low heart rate, and dizziness.
Coversyl (perindopril) shares traits with Aceon. It is an ACE inhibitor used primarily for hypertension and heart protection. Side effects are typical for ACE inhibitors.
Cozaar (losartan) is an ARB known to reduce stroke risk and protect kidneys in diabetic patients. It is well tolerated with minimal side effects.
Diltiazem works as a calcium channel blocker to relax blood vessels and reduce heart workload. It is effective for hypertension and some arrhythmias.
Esidrix and Microzide (hydrochlorothiazide) are thiazide diuretics. They help reduce fluid retention and lower blood pressure. Thiazides are often first-line options, but may lead to electrolyte imbalance.
Frumil is a combination of a loop diuretic and potassium-sparing agent. It is potent for fluid overload but requires monitoring of potassium levels.
Hytrin (terazosin) is an alpha-blocker. It relaxes vessels and is also used in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Side effects can include dizziness and fainting, especially after the first dose.
Hyzaar combines losartan and hydrochlorothiazide. This combination targets blood pressure through dual pathways. It usually causes fewer side effects compared to higher doses of individual drugs.
Inderal and Inderal LA (propranolol) are beta-blockers used to manage hypertension, angina, and migraines. They are non-selective and may cause fatigue or cold extremities.
Isoptin and Isoptin SR (verapamil) manage hypertension and angina. Extended-release versions improve convenience and compliance.
Lasix (furosemide) is a loop diuretic used in cases of severe fluid overload and hypertension. It is powerful but may cause electrolyte imbalances and dehydration.
Lisinopril is another popular ACE inhibitor. It lowers blood pressure and protects organs. Patients should monitor kidney function and potassium levels during treatment.
Lopressor (metoprolol tartrate) is a beta-blocker useful for controlling heart rate and blood pressure. It is taken multiple times daily.
Lozol (indapamide) is a thiazide-like diuretic. It treats hypertension and edema with fewer metabolic side effects than traditional thiazides.
Micardis (telmisartan) is an ARB with a long duration of action. It may provide added protection for patients with cardiovascular risk.
Minipress (prazosin) is an alpha-blocker for hypertension and sometimes PTSD symptoms. It has a pronounced first-dose effect requiring cautious titration.
Norvasc (amlodipine) is a widely used calcium channel blocker. It is effective, safe, and taken once daily. Side effects often include swelling of the legs and flushing.
Prinivil (lisinopril) shares characteristics with other ACE inhibitors. It is affordable and widely prescribed for hypertension.
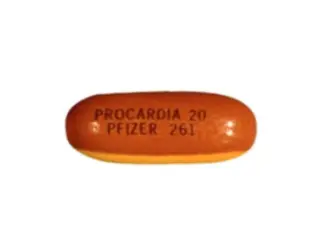
Procardia (nifedipine) provides quick blood pressure relief and angina control. Sustained-release forms offer improved safety and convenience.
Tenormin (atenolol) is a beta-1 selective blocker. It lowers blood pressure with fewer respiratory side effects. It may cause fatigue or cold extremities.
Toprol and Toprol XL (metoprolol succinate) are cardioselective beta-blockers. The XL form is extended-release, improving compliance. These drugs control heart rate and blood pressure well.
Trandate (labetalol) blocks both alpha and beta receptors. It is effective in hypertensive emergencies and pregnancy-related hypertension. Side effects include dizziness and fatigue.
Tritace (ramipril) resembles Altace in function and is effective in heart and kidney protection.
Vasotec (enalapril) is an ACE inhibitor that reduces blood pressure and heart strain. Common effects include cough and low blood pressure symptoms.
Verampil and Verapamil are calcium channel blockers that also help with certain arrhythmias and angina. Verapamil may cause constipation and swelling.
Zebeta (bisoprolol) is a selective beta-blocker that controls blood pressure with a low risk of respiratory side effects. It is usually well tolerated.
Zestoretic and Zestril combine lisinopril with hydrochlorothiazide or exist as lisinopril, respectively. These agents offer effective blood pressure control with benefits from both ACE inhibition and diuresis.
In conclusion, the choice of blood pressure medication depends on individual health conditions, comorbidities, and tolerability. Many options exist, each with unique benefits and side effects. Regular monitoring and doctor consultation are essential for optimal management.